Preprint: Brain imaging before and after Covid in UK Biobank
We identified .. a more pronounced reduction in grey matter thickness, and … a greater reduction in global measures of brain size and increase in cerebrospinal fluid volume.
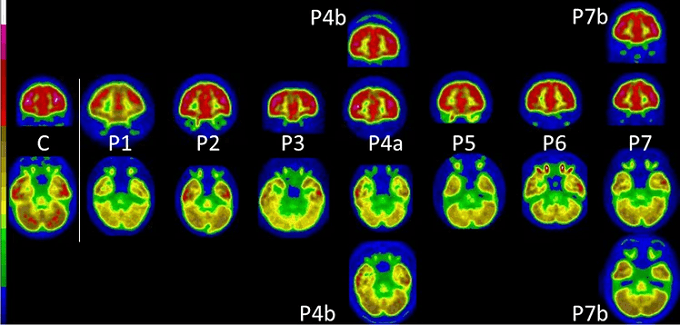
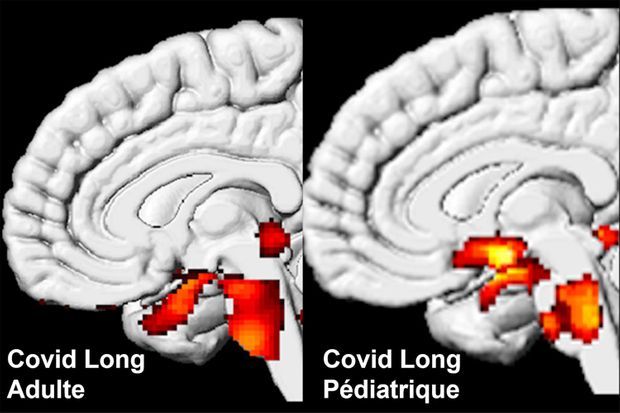
“we identified respectively 68 and 67 significant longitudinal effects associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in the brain, including, on average: (i) a more pronounced reduction in grey matter thickness and contrast in the lateral orbitofrontal cortex (min P=1.7×10 -4 , r=-0.14) and parahippocampal gyrus (min P=2.7×10 -4 , r=-0.13), (ii) a relative increase of diffusion indices, a marker of tissue damage, in the regions of the brain functionally-connected to the piriform cortex, anterior olfactory nucleus and olfactory tubercle (min P=2.2×10 -5 , r=0.16), and (iii) greater reduction in global measures of brain size and increase in cerebrospinal fluid volume suggesting an additional diffuse atrophy in the infected participants (min P=4.0×10 -6 , r=-0.17). When looking over the entire cortical surface, these grey matter thickness results covered the parahippocampal gyrus and the lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and extended to the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex, supramarginal gyrus and temporal pole. The increase of a diffusion index (mean diffusivity) meanwhile could be seen voxel-wise mainly in the medial and lateral orbitofrontal cortex, the anterior insula, the anterior cingulate cortex and the amygdala”
Preprint: Brain imaging before and after COVID-19 in UK Biobank