Preprint: Beta-amyloid deposits found in brains of young Covid patients
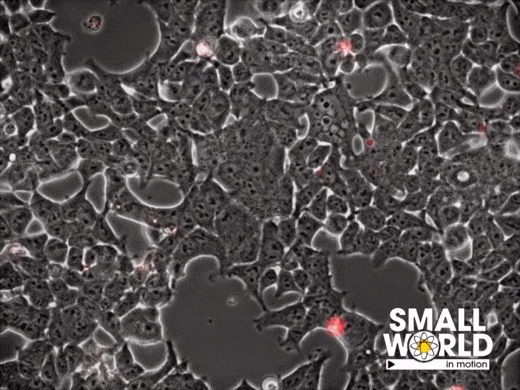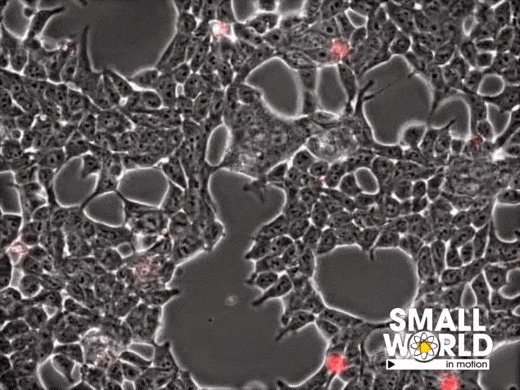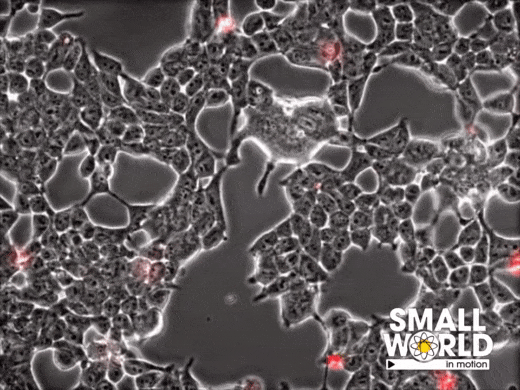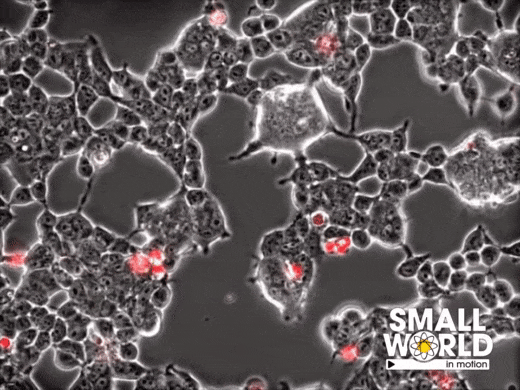
This report describes a relatively young (< 60 y/o) COVID patient without known clinical evidence of dementia who at autopsy had large numbers of thioflavin-negative, immunoreactive β-amyloid deposits in her neocortex.
In a small convenience cohort, 10 out of 10 COVID additional patients of a similar age range who came to autopsy had this pathology. We deliberately examined the cortex of patients in this age group because they are far less likely to contain β-amyloid deposits than older patients.”
Preprint: Β-Amyloid Deposits in Young COVID Patients
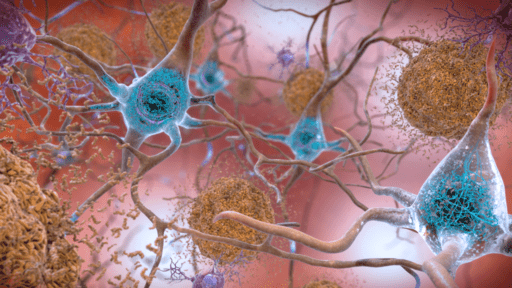
Amyloid plaques (also known as neuritic plaques, Aβ plaques or senile plaques) are extracellular deposits of the amyloid beta (Aβ) protein mainly in the grey matter of the brain. Degenerative neuronal elements and an abundance of microglia and astrocytes can be associated with amyloid plaques. Some plaques occur in the brain as a result of senescence (ageing), but large numbers of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are characteristic features of Alzheimer’s disease.
Preprint: SARS-CoV-2 invades the brain and activates an Alzheimers-like program
Image by NIH Image Gallery from Bethesda, Maryland, USA, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons